According to the official WeChat account of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, on February 28, 2024, China conquered the world's mainstream high-power heavy-duty gas turbine technology and independently developed the first prototype of a 300 MW F-class heavy-duty gas turbine, which was assembled and produced in Lingang, Shanghai. China's heavy-duty gas turbines have finally broken through and reached the global mainstream level, further narrowing the gap with GE and Siemens.
300 MW F-class reignition offline ceremony
The implementation entity of this project is State Power Investment Corporation of China, and the specific implementation is undertaken by China United Heavy Duty Gas Turbine Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as United Heavy Duty Combustion Company). The heavy-duty gas turbine is a major national project. The first prototype produced this time was assembled and manufactured by Shanghai Electric Group, with the participation of more than 200 enterprises, research institutes, universities and other companies from 19 provinces and cities including Beijing, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, etc. The entire line has overcome multiple key core technologies such as high-temperature alloy material development, control system design, component and whole machine design, and hot end component manufacturing. On November 27, 2020, the first 50 MW F-class heavy-duty gas turbine independently developed by Dongfang Electric Group in China successfully achieved full load stable operation. Strictly speaking, this gas turbine is of medium to large size, with over 20000 components. The F-class 300 MW heavy-duty gas turbine has over 50000 parts and a total of five major systems.
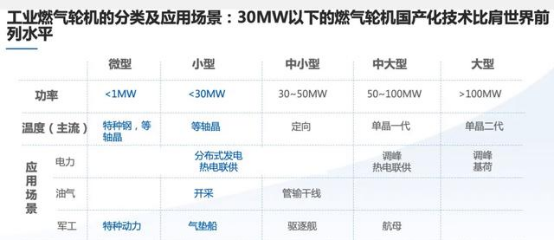
According to the working temperature of gas, heavy-duty gas turbines can be divided into E class, F class, G/H class, and J class, with gas working temperatures of 1200 ℃, 1400 ℃, 1500 ℃, and 1600 ℃ respectively. Among them, F class is currently the mainstream model in service, and generally more than 100 MW is considered a heavy-duty gas turbine. The four giants that monopolize heavy-duty gas turbines internationally are GE General Motors, Siemens, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries of Japan, and Ansaldo of Italy.
Classification of gas turbines
At present, the most advanced gas turbine in the world is the universal 9HA type, with a power of up to 826 megawatts, and it is also the most thermally efficient gas turbine in the world. Next is Mitsubishi Heavy Industries' M701 and J-type reignition engines, which have a power output of 650 megawatts. Due to the use of high-performance film cooling technology and special ceramic coatings, the M701 reignition engine has achieved the world's highest inlet temperature of 1600 degrees Celsius. Siemens' SGT5-8000H super gas turbine, although with a power output of 595 megawatts lower than that of General Mitsubishi, only requires one generator to meet the electricity consumption of a city.
The leading domestic enterprise in the field of advanced technology is undoubtedly Dongfang Electric, which first developed the F-class 50 MW gas turbine. Dongqi also obtained M701 and J-type reignition from Mitsubishi. In February 2022, China's * 690MW class J-type reignition successfully rolled off the production line, and Dongfang Electric became the * first domestic enterprise to control the entire E, F, and J-type reignition industry line. In 2023, the HA class heavy-duty gas turbine jointly produced by Harbin Electric Power and General Motors of the United States will be rolled off the production line in Qinhuangdao. This is almost the world's most powerful and highly efficient heavy-duty gas turbine, with a power of 838 megawatts for the 9HA.02 gas turbine, equivalent to 1000 megawatts of coal-fired power generation units in China.
China has designated heavy combustion as a major project and plans to conquer the world's largest 400 MW H-class gas turbines by 2030. The first prototype of the F-class 300 MW heavy-duty gas turbine has been produced, which is an important milestone in the independent innovation and development of heavy-duty gas turbines in China. It marks the completion of the manufacturing process based on forward design for high-power heavy-duty gas turbines and the entry into the final stage of whole machine testing and verification.
Note: The content and data of this article are mainly sourced from publicly available information of relevant enterprises and websites, and are for browsing purposes only.